Floor Of Mouth Swelling Differential Diagnosis

The floor of the mouth is the part of the oral cavity that is located under the tongue.
Floor of mouth swelling differential diagnosis. The differential diagnosis of dermoid cysts inludes infections of the floor of the mouth ranula infection ofthe submandibular or sublingual glands blockage of wharton s duct cystic hygroma thyoglossal duct cyst branchial cleft cyst benign and malignant tumors of the floor of the mouth and a detached branchogenic cyst 5 6 14 dermoid. Early on the floor of the mouth is raised and there is difficulty swallowing saliva which may run from the person s mouth. When the neck is involved thyroglossal cyst branchial cleft cyst cystic hygroma hemangioma lymphangioma or acute inflammatory lymphadenopathy should be considered in the differential diagnoses 4 6. Ludwig s angina often follows a tooth infection or other infection or injury in the mouth.
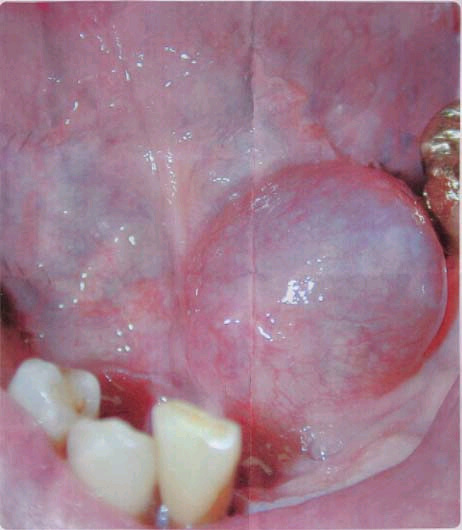
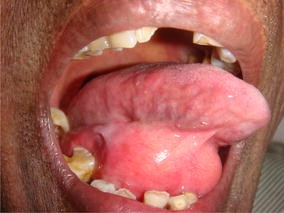
Usually included in the differential diagnosis of painless and slowly growing intraoral masses. The mucosal surface of the floor of the mouth is easily examined clinically as superficial abnormalities can be assessed visually without the aid of imaging. The symptoms include swelling of the tongue neck pain and breathing problems. The commonest swellings in.
This condition has a rapid onset over hours. Mouth sores and ulcers. Angina ludovici is a type of severe cellulitis involving the floor of the mouth. However salivary gland neoplasms of the floor of the mouth are more often malignant than benign 4 the present patient s age con forms to the higher incidence of salivary gland neo plasms 1 4 12 however the posterior hard palate soft palate.
List of 30 causes for mouth swelling and swelling of floor of the mouth alternative diagnoses rare causes misdiagnoses patient stories and much more. Butterfly shaped rash across the cheeks and nose. Floor of mouth swellings in the floor of the mouth are more likely to arise from structures above the mylohyoid muscle than below it. As the condition worsens the airway may be compromised with hardening of the spaces on both sides of the tongue.
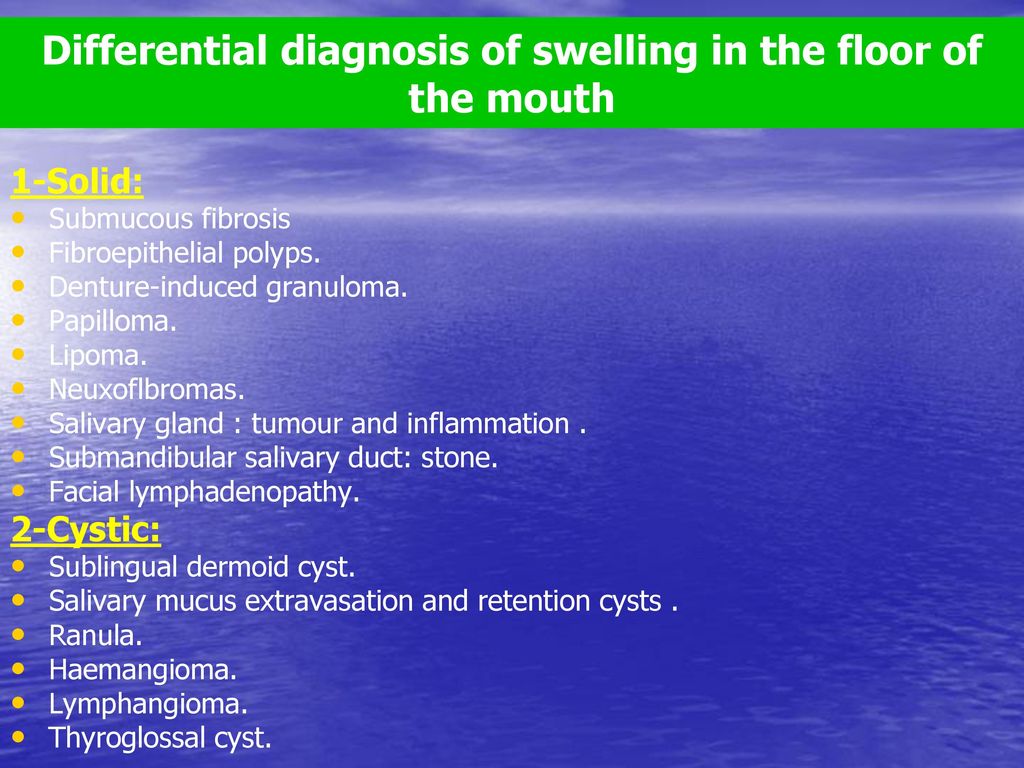
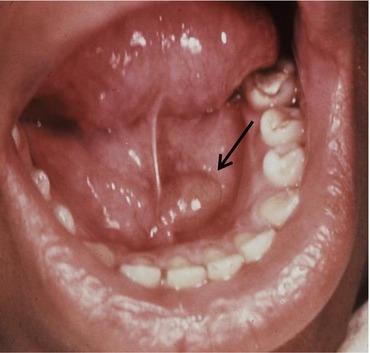
It may be involved in a wide range of pathologic processes some of which are unique to the region. Other differential diagnoses of cystic lesions at the floor of the mouth are ranula dermoid and epidermoid cysts soft nodular lesions with sessile base lipoma asymptomatic yellowish mass with doughy feel vascular lymphatic malformations usually in infants soft and compressible mass wharton duct blockage pain and swelling of the affected salivary gland which get worse with chewing.