Floor Diaphragm Meaning

Diaphragm 5 type rigid height 14 15.
Floor diaphragm meaning. Diaphragm 4 type rigid height 10 95. The term diaphragm includes horizontal bracing systems. Similar to a shear panel a horizontal diaphragm is a horizontal truss in a roof plane or solid sheet element in a floor. A horizontal diaphragm element parallel and in line with the applied force that collects and transfers diaphragm shear forces to the vertical elements of the lateral force resisting system and or distributes forces within the diaphragm.
Diaphragm 2 type rigid height 4 55. Diaphragm definition is a body partition of muscle and connective tissue. Diaphragms are usually constructed of plywood or oriented strand board in timber construction. Opening at the edge of a floor may weaken the diaphragm just as a notch in a flange weakens a beam.
Diaphragm is horizontal or nearly horizontal system acting to transmit lateral forces to the vertical resisting elements. The diaphragm of a structure often does double duty as the floor system or roof system in a building or the deck of a bridge which simultaneously supports gravity loads. Or a concrete slab in. A horizontal system roof floor or other membrane or horizontal bracing acting to.
Diaphragm 6 type rigid height 17 35. Flexible frames rigid walls an important characteristic of diaphragms is flexibility or its opposite rigidity. There are two popular types of diaphragm namely rigid diaphragm and semi rigid diaphragm. Metal deck or composite metal deck in steel construction.
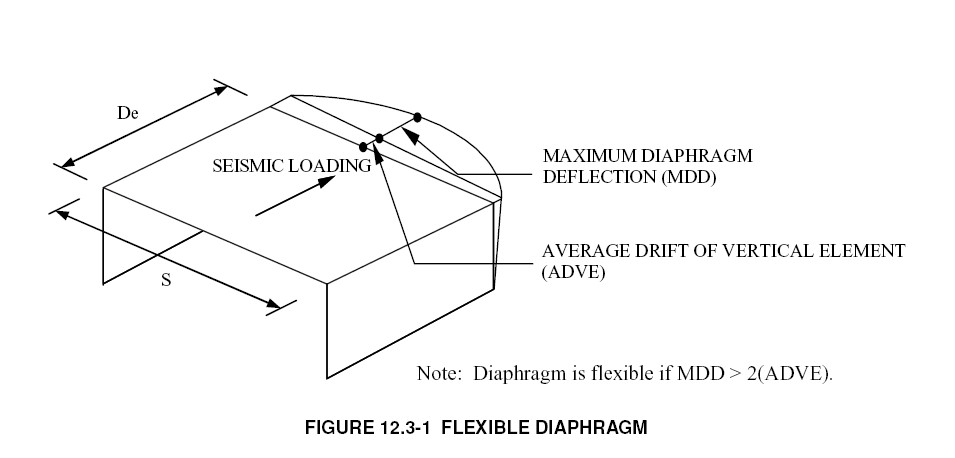
The rigid diaphragm can rotate and it can translate but cannot deform. Diaphragm 3 type rigid height 7 75. Diaphragm is determined to be more than two times the average deflection of the vertical resistant elements the diaphragms may be considered as being flexible. In timber floors for example the floor sheeting carries the shear forces while perimeter joists.
In seismic design rigidity means relative rigidity. The results show that there can be significant flanking due to the structural path through the floor when there is continuous plywood. Of importance is the in plane rigidity of the diaphragm. The floor diaphragm command can be defined in the following manner.
In fact the calculations indicated that for coupled structures the most important noise path is from the source room into the floor through the diaphragm into the adjacent floor and into the receiving room.