Explain Seafloor Spreading In Terms Of Movement At A Plate Boundary

Plate tectonics plate tectonics seafloor spreading.
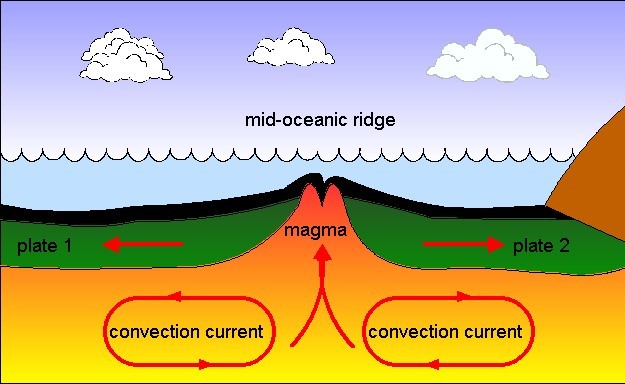
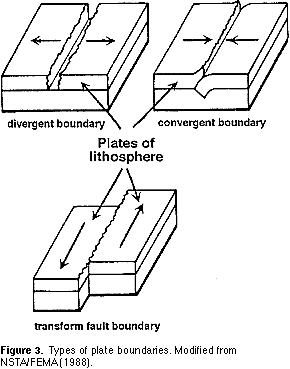
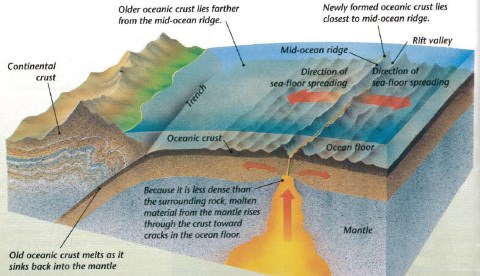
Explain seafloor spreading in terms of movement at a plate boundary. Seafloor spreading seafloor spreading is the movement of two oceanic plates away from each other at a divergent plate boundary which results in the formation of new oceanic crust from magma that comes from within the earth s mantle along a a mid ocean ridge. Seafloor spreading helps to explain continental drift in the theory of plate tectonics. When two plates come together it is known as a convergent boundary. When oceanic plates diverge tensional stress causes fractures to occur in the lithosphere.
Seafloor spreading seafloor spreading is identified as the movement of two oceanic plates away from each other. The mid atlantic ridge for instance separates the north american plate from the eurasian plate and the south american plate from the african plate the east pacific rise is a mid ocean ridge that runs through the eastern pacific ocean and separates the pacific plate from the north american. This crust forms from the magma that comes from within the earth s mantle when the two plates split away from each other. The impact of the colliding plates can cause the edges of one or both plates to buckle up into a mountain ranges or one of the plates may bend down into a deep seafloor trench.
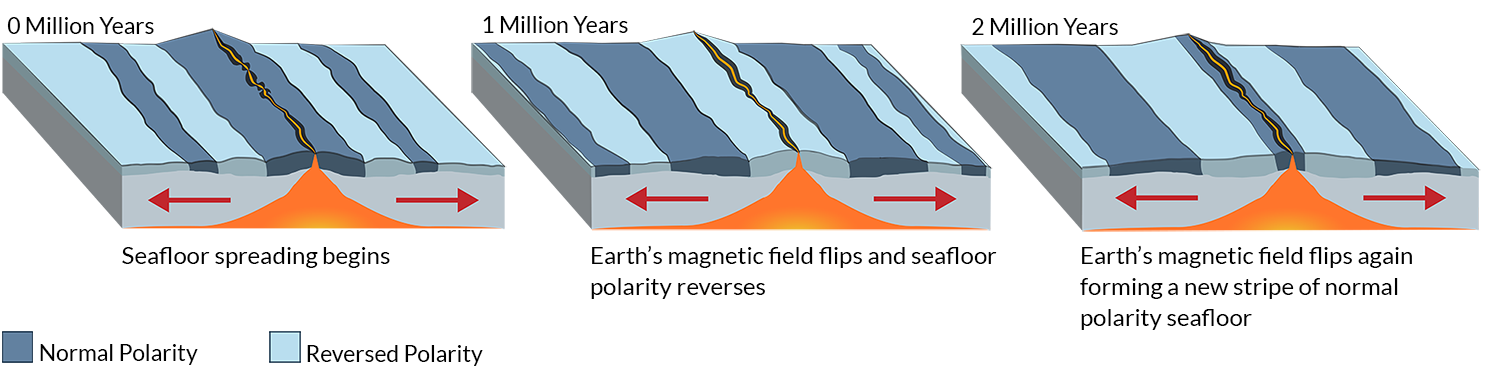
Seafloor spreading occurs along mid ocean ridges large mountain ranges rising from the ocean floor. What results from this is the formation of a new oceanic crust. As upwelling of magma continues the plates continue to diverge a process known as seafloor spreading. These age data also allow the rate of seafloor spreading to be.