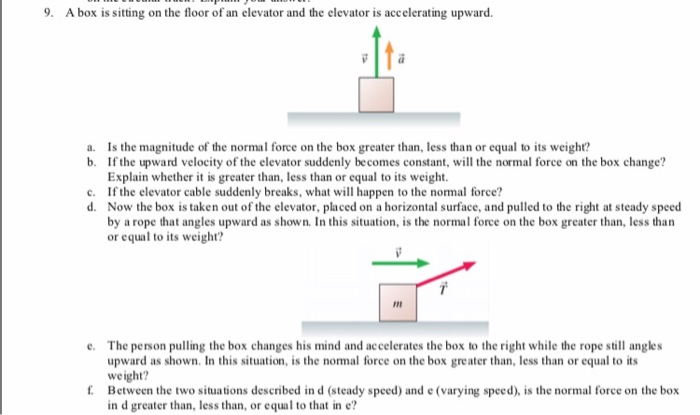
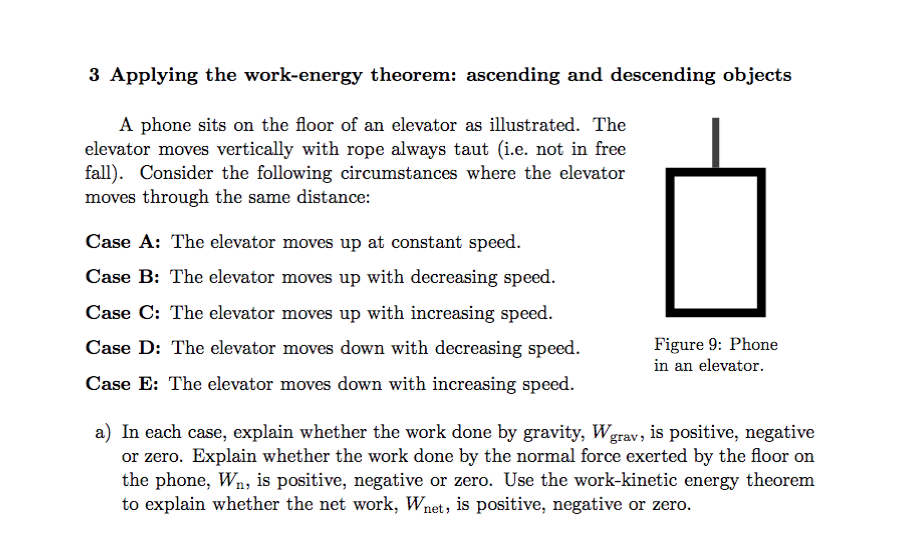
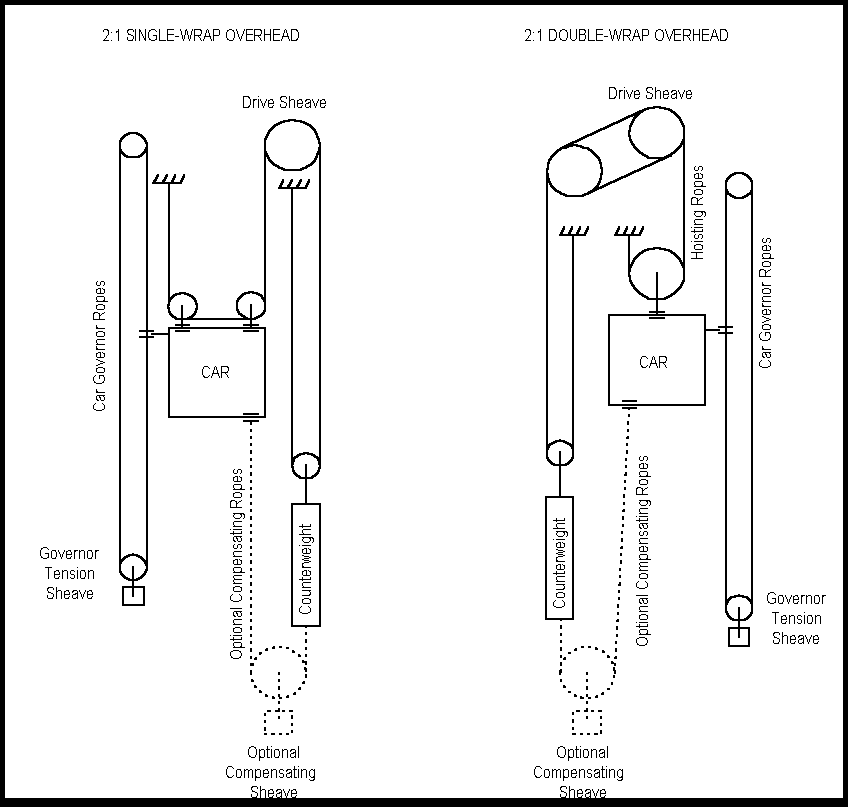
Elevator Force Of Floor Force Of Rope

Force along the surface.
Elevator force of floor force of rope. Example force and power to lift an elevator. The elevator acceleration of the elevator is negative downward increasing the velocity magnitude in the downward direction. The elevator s free body diagram has three forces the force of gravity a downward normal force from you and an upward force from the tension in the cable holding the elevator. The force required to move the elevator at constant speed can be calculated as.
The elevator then speeds up in the downward direction towards a lower floor. In technical terms traction is the frictional force. So that force would be an equal force but in the opposite direction. A higher force pulling on the rope results in a higher tension for example if the elevator were on a more massive planet with a higher gravity or if someone stood below the fish and pulled downward on it.
The tension in the lower rope. An elevator with mass 2000 kg including passengers are moved from level 0 m to level 15 m. The elevator is moving downward at a constant speed. The inertia of the person would prefer to stay at rest so the elevator floor and scale effectively drop out a little bit from underneath.
Another such source of pulling force is if rather than the fish being accelerated downward the elevator were accelerated upward. Assume the elevator is at rest. So the a net a cable g. F c 2000 kg 9 81 m s 2 19820 n.
For example if the elevator is to be in free fall 9 8 m s 2 the. It discusses how to calculate the apparent weight. The counter weight is placed either at the side or rear with respect to the car position in the hoistway shaft. Force of the piano on the floor force of chadwick on the piano.
So it just completely bounces off. So that net force in this situation is the force of the floor of the elevator supporting the toddler. For each of the following situations select the correct relationship between the magnitudes of the two forces given. Find t1 the tension in the upper rope.
Two blocks are stacked on top of each other on the floor of an elevator. So in this case the normal force is 98 newtons in the j direction. This physics video tutorial explains how to find the normal force on a scale in a typical elevator problem. Starting with the elevator basics the elevator system first consists of the car which carries the passengers to the destination floor.
And in this case that would be the normal force. The combined system of you elevator has two forces a combined force of gravity and the tension in the cable. Assume the blocks are at rest. So when the elevator has a net acceleration of 1 2 m s 2 upward that means it has to supply that much more force.
Rank the magnitude of the forces.