Effect Of Porosity On Mechanical Properties Of Ceramics

The aim of this chapter is to review the mechanical properties of macro porous ceramics.
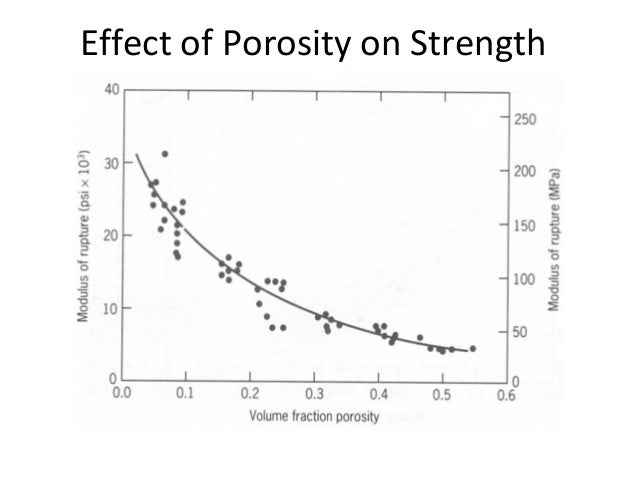
Effect of porosity on mechanical properties of ceramics. These properties have many uses comprehending macroscaled devices mesoscaled materials and microscaled pieces. D 50 nm. Porous zrb 2 sic zs ceramics with different volume fractions of porosity i e. D 2 nm.
The following issues are of particular interest to this paper. This special issue gathers the most recent and major scientific progress on studying the effect of porosity on the mechanical properties of ceramics. It is widely known that increasing interest in porous ceramics is due to their special properties which comprise high volumetric porosity up to 90 with open or closed pores and a broad range of pore sizes micropores. The book elucidates the fundamental interrelationships determining the development and use of materials for actual and potential engineering needs.
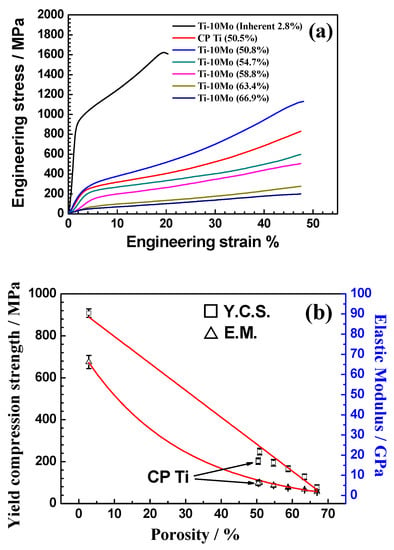
Rice husk consists of ash 17 23 fixed carbon 10 15 and volatile matter 60 65. 8 7 17 9 and 27 3 and different mean pore diameter i e. The porosity density mechanical properties and pore size distribution of porous ceramics generally rice husk plays a role in the formation of pores due to the nature of its composition. 2 21 3 65 and 4 23 μm were fabricated using partial hot pressing in order to investigate the effect of the porosity and pore size on their mechanical and thermal properties as well as thermal shock performance.
50 nm d 2 nm and macropores. However for porous β sialon ceramics it is important to introduce the uniformly distributed porosity and pore size with appropriate phase assemblage of si 6 z al z o z n 8 z 0 z 4 to meet specific application demands especially combination of low dielectric constant without compromising mechanical properties. Focuses on the effects of porosity and microcracking on the physical properties of ceramics particularly nominally single phase ceramics. Mechanical tests are performed to assess the role of the matrix in both matrix dominated and fiber dominated loading configurations.
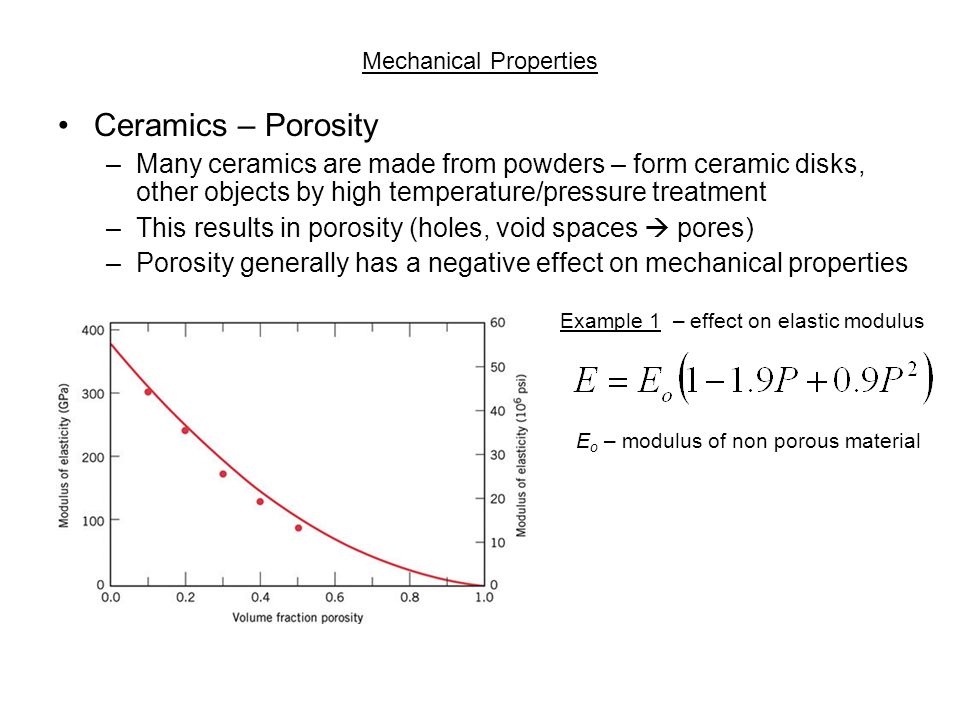
The purpose of this article is to review in detail the factors affecting the porosity of ceramic material such as pore forming agents the mechanical properties and methods available to. The effects of matrix porosity on the mechanical properties of an all oxide ceramic composite are investigated.